Discount rate; likewise called the obstacle rate, cost of capital, or needed rate of return; is the expected rate of return for an investment. In other words, this is the interest portion that a business or investor anticipates getting over the life of an investment. It can likewise be thought about the rates of interest utilized to determine the present value of future capital. Thus, it's a required component of any present value or future value computation (Which of these is the best description of personal finance). Financiers, bankers, and company management use this rate to evaluate whether a financial investment deserves considering or should be disposed of. For example, an investor may have $10,000 to invest and need to get at least a 7 percent return over the next 5 years in order to meet his objective.
It's the amount that the financier needs in order to make the investment. The discount rate is most frequently used in calculating present and future values of annuities. For example, an investor can utilize this rate to calculate what his investment will deserve in the future. If he puts in $10,000 today, it will deserve about $26,000 in ten years with a 10 percent rate of interest. Conversely, an investor can utilize this rate to compute the amount of money he will require to invest today in order to satisfy a future financial investment goal. If a financier wishes to have $30,000 in 5 years and presumes he can get a rates of interest of 5 percent, he will have to invest about $23,500 today.
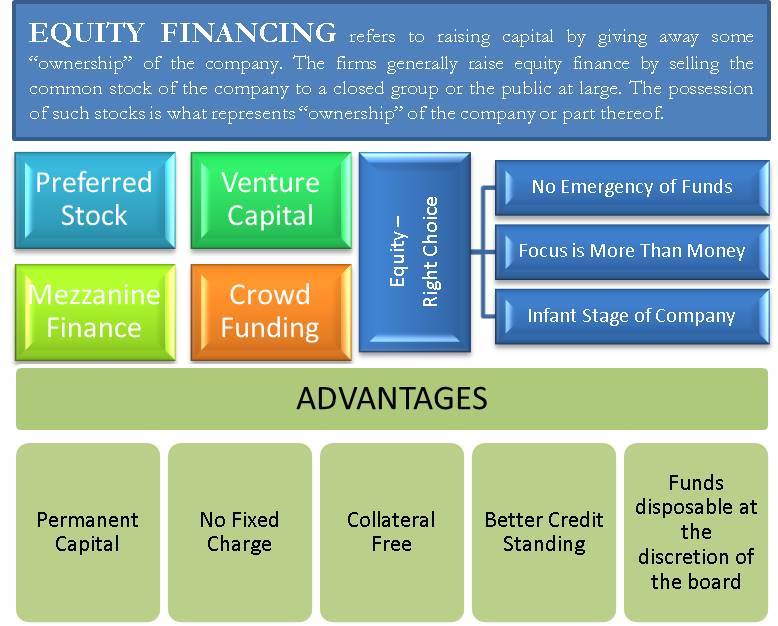
The truth is that business use this rate to determine the return on capital, inventory, and anything else they invest money in. For instance, a producer that invests in brand-new devices might require a rate of at least 9 percent in order to break even on the purchase. If the 9 percent minimum isn't fulfilled, they might change their production procedures appropriately. Contents.
Definition: The discount rate refers to the Federal Reserve's rate of interest for short-term loans to banks, or the rate used in an affordable cash circulation analysis to determine net present worth.
Discounting is a financial mechanism in which a debtor gets the right to postpone payments to a lender, for a specified time period, in exchange for a charge or fee. Basically, the celebration that owes money in the present purchases the right to delay the payment until some future date (What does nav stand for in finance). This transaction is based on the reality that the majority of people choose current interest to delayed interest because of mortality get out of timeshare results, impatience results, and salience results. The discount, or charge, is the distinction between the original quantity owed in today and the amount that needs to be paid in the future to settle the debt.
The discount yield is the proportional share of the initial amount owed (initial liability) that must be paid to postpone payment for 1 year. Discount yield = Charge to delay payment for 1 year debt liability \ displaystyle ext Discount yield = \ frac ext Charge to delay payment for 1 year ext debt liability Because an individual can make a return on money invested over some amount of time, the majority of financial and monetary designs assume the discount rate yield is the same as the rate of return the person might receive by investing this cash in other places (in properties of similar risk) over the offered time period covered by the hold-up in payment.
The relationship in between the discount rate yield and the rate of return on other monetary assets is usually talked about in economic and monetary theories including the inter-relation between different market value, and the accomplishment of Pareto optimality through the operations in the capitalistic price system, as well as in the conversation of the effective (financial) market hypothesis. The person postponing the payment of the current liability is basically compensating the individual to whom he/she owes cash for the lost income that might be earned from a financial investment during the time period covered by the delay in payment. Accordingly, it is the appropriate "discount yield" that determines the https://plattevalley.newschannelnebraska.com/story/43143561/wesley-financial-group-responds-to-legitimacy-accusations "discount rate", and not the other method around.
What Does Ear Stand For In Finance Fundamentals Explained
Because an investor makes a return on the initial principal quantity of the financial investment in addition to on any prior duration investment income, financial investment profits are "compounded" as time advances. For that reason, considering the truth that the "discount" must match the benefits obtained from a similar financial investment possession, the "discount rate yield" must be utilized within the exact same compounding mechanism to work out an increase in the size of the "discount rate" whenever the time period of the payment is delayed or extended. The "discount rate" is the rate at which the "discount" should grow as the hold-up in payment is extended. This truth is directly connected into the time value of cash and its estimations.
Curves representing constant discount rates of 2%, 3%, 5%, and 7% The "time value of money" indicates there is a difference in between the "future worth" of a payment and the "present value" of the same payment. The rate of roi need to be the dominant consider assessing the market's assessment of the distinction in between the future worth and the present worth of a payment; and it is the marketplace's assessment that counts one of the most. Therefore, the "discount rate yield", which is predetermined by an associated roi that is discovered in the monetary markets, is what is used within the time-value-of-money calculations to figure out the "discount" required to delay payment of a monetary liability for an offered time period.
\ displaystyle ext Discount rate =P( 1+ r) t -P. We want to determine the present value, likewise called the "affordable worth" of a payment. Keep in mind that a payment made in the future deserves less than the very same payment made Click here today which could immediately be transferred into a checking account and make interest, or purchase other assets. For this reason we need to mark down future payments. Think about a payment F that is to be made t years in the future, we determine the present worth as P = F (1 + r) t \ displaystyle P= \ frac F (1+ r) t Suppose that we wanted to discover today value, represented PV of $100 that will be gotten in five years time.
12) 5 = $ 56. 74. \ displaystyle \ rm PV = \ frac \$ 100 (1 +0. 12) 5 =\$ 56. 74. The discount rate which is used in financial computations is normally chosen to be equal to the cost of capital. The expense of capital, in a monetary market equilibrium, will be the very same as the market rate of return on the financial asset mix the company utilizes to finance capital expense. Some change may be made to the discount rate to appraise risks associated with unpredictable capital, with other developments. The discount rates normally used to various kinds of business show considerable distinctions: Start-ups looking for cash: 50100% Early start-ups: 4060% Late start-ups: 3050% Fully grown business: 1025% The greater discount rate for start-ups reflects the numerous downsides they deal with, compared to recognized business: Lowered marketability of ownerships due to the fact that stocks are not traded publicly Little number of investors ready to invest High risks connected with start-ups Extremely optimistic forecasts by enthusiastic creators One method that looks into an appropriate discount rate is the capital possession pricing model.